Introduction: The Unseen Force Behind Your Timepiece’s Performance
For collectors of automatic watches, a quality watch winder serves as an essential companion to keep timepieces running smoothly when not being worn. At the heart of every watch winder lies its motor—the critical component that determines how effectively your precious timepiece maintains its accuracy and functionality.
The motor power of a watch winder doesn’t just influence how it operates; it directly impacts the long-term performance and longevity of your automatic watches. Without proper, consistent motion (typically 650-800 turns per day), automatic watches lose their power reserve and eventually stop, requiring manual resetting when you decide to wear them again.
Understanding motor specifications might seem technical, but it’s actually quite straightforward when broken down. Whether you’re selecting your first winder or troubleshooting an existing one, knowing about motor types, performance metrics, and quality factors will help ensure your timepiece receives the care it deserves. Having a solid foundation for understanding motor specifications will guide you through the sometimes confusing world of watch winder technology.
What Makes a Watch Winder Motor Essential?
The motor in a watch winder performs one fundamental task: it simulates the natural motion of your wrist to keep automatic watches wound. Automatic watches contain a rotor that spins with movement, winding the mainspring that powers the watch. When not worn, these watches eventually run down—typically within 24-72 hours.
A quality watch winder motor solves this problem by creating consistent, controlled movement that keeps the watch’s power reserve topped up. Key attributes that define motor performance include:
- Power source reliability (AC, battery, or USB)
- Rotation programming capabilities
- Consistency in maintaining proper speeds
- Ability to change direction (clockwise, counterclockwise, or bidirectional)
Without a properly functioning motor, watches may receive inadequate winding, inconsistent movement, or potentially damaging excessive rotation. Many people mistakenly believe any rotation will suffice, but automatic watches require specific winding parameters to maintain optimal performance.
The motor essentially powers the entire rotation mechanism that turns the watch cushions. Understanding the types of motors in watch winders provides insight into which option might best suit your collection’s needs.
Types of Watch Winder Motors: Understanding Your Options
Power Source Variations
The power source of a watch winder motor significantly impacts its placement flexibility, reliability, and convenience.
AC-Powered Motors:
– Provide consistent, uninterrupted power for continuous operation
– Never require battery replacement
– Typically found in premium or multi-watch winders
– Limited by need for proximity to electrical outlets
– Often feature slightly more powerful motors
Battery-Powered Motors:
– Offer complete placement flexibility
– Run for approximately 3-6 months on fresh batteries
– Perfect for travel or areas without reliable electricity
– May experience power fluctuation as batteries deplete
– Typically require C or D batteries for extended operation
USB-Powered Motors:
– Represent the modern approach to winder power
– Can be powered by wall adapters, computers, or power banks
– Often feature more precise digital controls
– May have limitations in power output compared to AC
– Increasingly common in contemporary winder designs
Dual/Hybrid Power Systems:
– Combine benefits of multiple power sources
– Allow for seamless transition between power options
– Provide backup power during outages
– Typically command premium pricing
– Offer maximum flexibility for placement and usage
Understanding how much electricity watch winders use can help you make an informed decision about which power source best suits your needs and usage habits.
Drive Mechanism Distinctions
The way a motor transfers power to the rotation system significantly impacts operation quality, noise levels, and longevity.
Direct Drive Systems:
– Motor directly powers the rotation cup
– Fewer moving parts means less potential for mechanical failure
– May transmit more motor vibration to the watch
– Often found in compact or entry-level winders
– Typically produce more noticeable operation sound
Belt-Driven Systems:
– Use a belt to transfer power from motor to rotation mechanism
– Belt absorbs vibration, creating smoother operation
– Provides natural cushioning for watches
– Slightly less efficient power transfer
– Belts may require occasional replacement after years of use
Gear-Driven Systems:
– Utilize precision gears to transfer and control motion
– Common in high-end European and Japanese winders
– Provide extremely precise rotation control
– Often operate more quietly than direct drive systems
– Typically last longer with proper maintenance
For those sensitive to noise, understanding the ultimate guide to quiet watch winders can help identify the drive mechanism that will be least disruptive in your home environment.
Motor Quality Classifications
Not all watch winder motors are created equal, with significant variance in quality, reliability, and performance.
Premium Japanese Motors (including Mabuchi):
– Industry standard for reliability and performance
– Typically operate below 10 decibels (virtually silent)
– Precision-engineered for consistent rotation speed
– Expected lifespan of 8-10+ years of regular operation
– Found in most mid-to-high-end winders
High-Performance European Motors:
– Often Swiss or German-engineered components
– Exceptional precision in maintaining exact rotation parameters
– Typically feature ball-bearing construction for smoothness
– May include advanced programming capabilities
– Command premium pricing but deliver unmatched reliability
Standard/Budget Motors:
– Adequate performance for basic winding needs
– May produce more noise (15-25 decibels)
– Typically last 2-5 years before showing wear
– Less consistent rotation speeds as power fluctuates
– More susceptible to temperature and humidity variations
Quality indicators often transcend branding, with physical traits like motor weight, bearing quality, and vibration dampening providing clues to overall performance. For enthusiasts seeking the best, exploring high-performance winder motors guide provides detailed specifications to look for when evaluating options.
Critical Performance Metrics: Ensuring Proper Winding
Understanding Turns Per Day (TPD)
Turns Per Day (TPD) represents the most critical performance metric for watch winder motors. This measurement indicates how many complete rotations the winder performs in a 24-hour period, directly impacting how effectively your watch maintains its power reserve.
Different watch movements have specific TPD requirements. For example, most Rolex movements function best with 650-750 TPD, while some Omega calibers may require 800+ TPD. The motor’s ability to deliver these precise rotation counts consistently determines whether your watch receives proper winding.
Quality motors feature adjustable TPD settings, allowing customization for different watch brands and models. Budget winders often offer fixed settings that may not match your specific timepiece’s needs. Advanced motors maintain consistent rotation counts regardless of power source fluctuations, ensuring reliable performance.
A common misconception is that excessive TPD will overwind and damage an automatic watch. In reality, most modern automatic watches have slipping mainsprings that prevent overwinding. However, receiving insufficient TPD can cause a watch to lose accuracy or stop completely.

For those with diverse watch collections, understanding TPD requirements for watch winders ensures each timepiece receives its optimal winding parameters.
Rotation Direction Capabilities
The direction in which a watch winder rotates plays a crucial role in properly winding different watch movements. Quality motors must support multiple directional options:
- Clockwise (CW): Required by some watch movements
- Counterclockwise (CCW): Needed by other movement designs
- Bidirectional (Both CW and CCW): Universal coverage for most watches
- Alternating: Switches between directions at programmed intervals
Different watch brands engineer their automatic movements to wind in specific directions. For example, many Rolex watches wind efficiently in both directions, while some specialized movements wind primarily in one direction.
The motor design directly enables this directional control through its programming and mechanical configuration. Premium motors offer precise directional switching without jarring movements that could potentially damage delicate watch mechanisms.
For watch collectors with diverse collections, having a motor that supports all directional options provides maximum compatibility. Understanding how fast watch winders should spin complements directional knowledge for complete winding optimization.
Rotation Cycles and Rest Periods
Advanced watch winder motors don’t simply rotate continuously—they follow programmed cycles of operation and rest. This intermittent rotation pattern more closely mimics natural wear patterns and prevents potential stress on watch components.
Quality motors manage these cycles with precision, typically following patterns such as:
- 5 minutes rotation followed by 30-55 minutes rest
- 10 minutes rotation followed by 90 minutes rest
- Custom cycles based on specific watch requirements
The motor’s efficiency during these cycling operations impacts battery life in portable winders and overall wear on mechanical components. Superior motors maintain consistent rotation speeds throughout their active cycles, regardless of battery charge levels.
Sophisticated programming allows the motor to achieve the required TPD while minimizing continuous operation, closely mimicking the natural wearing experience. This approach promotes better long-term watch care than constant rotation.
Quality Indicators: What Separates Superior Motors
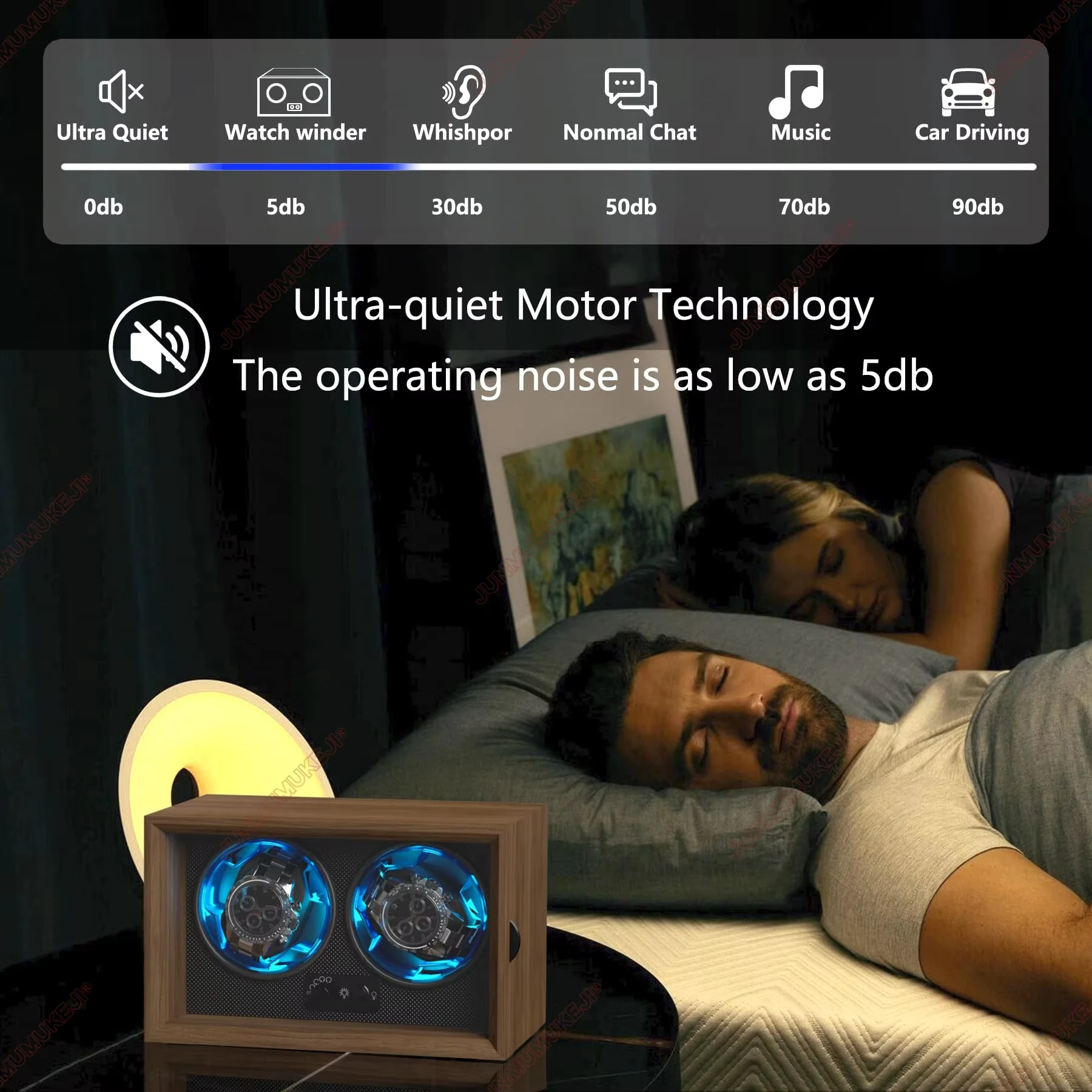
Noise Level and Operation Smoothness
A watch winder’s noise level often serves as the most immediately apparent indicator of motor quality. Premium motors operate virtually silently (under 10 decibels)—quieter than a whisper—while budget options may produce noticeable humming or clicking sounds.
Several technical factors influence motor noise:
- Bearing quality (ball bearings produce less noise than sleeve bearings)
- Motor mounting (rubber or silicone dampeners reduce vibration transfer)
- Gear precision (tighter tolerances reduce mechanical noise)
- Insulation materials surrounding the motor housing
The ideal placement for many watch winders—bedrooms, offices, or display areas—makes noise consideration particularly important. A winder that produces disruptive sound quickly becomes frustrating regardless of its technical specifications.
When evaluating potential winders, listening for smooth, consistent operation rather than irregular sounds indicating poor construction can help identify quality motors. Understanding watch winder motor durability factors provides insight into how construction quality relates to both noise and longevity.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
The durability of a watch winder motor largely determines the overall value proposition of the winder itself. Premium motors typically offer:
- Expected operational lifespan of 8-10+ years of daily use
- High-grade materials in gears and mechanical components
- Quality bearings that resist wear even with constant use
- Thermal management to prevent overheating
Maintenance requirements vary significantly between motor types:
- Premium motors generally require minimal maintenance beyond occasional dusting
- Belt-driven systems may need belt replacement after several years
- Budget motors might require more frequent internal cleaning to prevent dust buildup
- Battery-powered units need regular battery replacement to prevent leakage
Warning signs of motor deterioration include increased noise, inconsistent rotation speeds, or unusual vibration. Addressing these symptoms early can sometimes prevent complete failure.
For those interested in long-term reliability, exploring watch winder warranty and reliability factors provides valuable insights into which brands stand behind their motor quality.
Power Efficiency and Consistency
A quality watch winder motor balances performance with energy efficiency—a particularly important consideration for battery-powered units. Efficient motors:
- Consume minimal power while maintaining consistent performance
- Maintain stable rotation speeds regardless of power source condition
- Feature smart power management that optimizes energy use during rest periods
- Provide longer operation between battery changes
The practical impact of efficiency appears in battery life, with premium motors often delivering 2-3 times longer operation than budget alternatives using identical batteries. This efficiency translates to both convenience and reduced operating costs over time.
More importantly, consistent rotation speed ensures watches receive their required TPD regardless of battery condition or power fluctuations. Budget motors may slow down as batteries deplete, resulting in inadequate winding.

Making the Right Selection: Matching Motors to Your Needs
Watch Collection Compatibility
Selecting the right watch winder motor requires understanding the specific needs of your timepiece collection. Different watches have distinct winding requirements based on their movement design.
To determine your watches’ specific needs:
– Consult the manufacturer’s documentation for recommended TPD and direction
– Research your specific movement types online through watch enthusiast forums
– Consider the power reserve duration of your watches (longer reserves may need less frequent winding)
– Assess whether your collection has consistent needs or diverse requirements
For collectors with varied timepieces, motors offering customizable settings provide maximum flexibility. Some specialized watches with complex movements (like perpetual calendars or moon phases) may have specific winding recommendations to maintain all functions properly.
When facing compatibility questions or issues, exploring resources for troubleshooting common watch winder problems can provide guidance specific to different watch brands and movements.
Environmental and Placement Factors
Where and how you plan to use your watch winder significantly influences which motor type will work best for your situation.
Placement considerations include:
– Proximity to electrical outlets (affects power source options)
– Sensitivity to noise in the intended location (bedroom vs. closet)
– Space constraints that might limit winder size
– Visibility as part of a display or hidden storage
– Temperature and humidity variations in the placement area
For travel or locations with unreliable power, battery-operated motors provide essential flexibility. Conversely, homes with dedicated watch display areas might benefit from the consistency of AC-powered options.
Environmental factors also influence motor longevity, with extreme temperatures or humidity potentially affecting performance over time. Quality motors include protection against these variables for consistent operation.
Exploring automatic watch winder options with different form factors and power configurations can help identify the best match for your specific environment and placement needs.
Troubleshooting Common Motor Issues
Even quality watch winders may occasionally experience issues. Distinguishing between motor-specific problems and other winder malfunctions helps determine the appropriate solution.
Common motor-related symptoms include:
Complete failure to rotate: Often indicates power supply issues or motor failure
– Check power connections, batteries, or adapter functionality
– Ensure nothing is physically obstructing the rotation mechanism
– Listen for motor sounds to determine if it’s attempting to operateInconsistent rotation: Suggests motor control issues or power fluctuations
– Replace batteries if using battery power
– Test with different power sources if possible
– Check for loose connections in the power supplyUnusual noises: Generally indicate mechanical wear or obstruction
– Remove watches and test empty to isolate the source
– Check for foreign objects interfering with the mechanism
– Consider whether sounds have gradually increased (suggesting wear) or suddenly appeared (suggesting component failure)
For persistent issues, professional service might be required. However, before seeking replacement, exploring watch winders options can provide perspective on whether repair or replacement offers better value.
Automatic Watch Winder, Luxury Watch Winder, Single Watch Box
$307.39 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page4 Watch Winder, 6 Watch Box, Automatic Watch Winder
$512.31 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageAutomatic Watch Winder, Single Watch Winder, Wooden Watch Holder
$201.76 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageAutomatic Watch Winder, Leather Watch Travel Case, Single Watch Winder
$146.30 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageAutomatic Watch Winder, Double Watch Winder, Leather Watch Boxes
$147.60 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageAutomatic Watch Winder, Double Watch Winder
$206.18 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Advanced Considerations for Enthusiasts (Supplemental Content)
For technically-inclined collectors, watch winder motors offer interesting possibilities beyond standard usage. Some enthusiasts pursue motor upgrades for standard winders, enhancing performance or extending the life of otherwise quality units.
Replacement motors typically require matching voltage specifications (commonly 3V DC for standard units) and physical dimensions to ensure proper fit. Japanese-manufactured Mabuchi motors represent the most common replacement option, offering reliability and wide compatibility.
DIY enthusiasts might consider custom winder projects using specialized components, though this requires understanding both motor specifications and the specific needs of automatic watches. These projects typically involve sourcing small DC motors with gear reduction systems to achieve the slow, controlled rotation watches require.
For those interested in premium experiences, exploring luxury watch winder options provides insight into the highest quality motors and programming capabilities available.

Frequently Asked Questions
Can a quality motor extend my automatic watch’s lifespan?
Yes, a quality motor provides more consistent and gentle winding, reducing stress on your watch’s winding mechanism. This consistent care helps maintain optimal performance and potentially extends the interval between servicing.
How often should I replace batteries in my watch winder?
For quality winders, batteries typically last 3-6 months with regular use. It’s best to replace them proactively rather than waiting for complete depletion, which could lead to leakage. Some premium single watch winders feature battery level indicators to help time replacements appropriately.
Is it normal for watch winder motors to make some noise?
Some noise is normal, particularly in entry-level winders. However, quality motors should produce minimal sound—typically a soft, consistent hum rather than clicking or grinding noises. Premium winders operate almost silently (under 10 decibels).
Can I leave my watch winder running continuously?
While most quality winders are designed for continuous operation, using programmed rest periods more accurately mimics natural wear patterns and conserves power. Many experts recommend using rest period settings that allow the motor breaks between rotation cycles.
How do I know if my watch is receiving enough TPD?
The simplest test is observing whether your watch maintains accurate time after sitting on the winder. If it keeps proper time when you wear it after being on the winder, the TPD setting is likely adequate. If it’s losing time or has stopped, you may need to increase the TPD setting.